We were really hoping to see some ray tracing performance metrics together with the rest of the awesome graphs shown yesterday by Team Red during the RX 6000 GPU presentation, but, unfortunately, that did not happen. However, AMD chose to sneak some performance info in the footnotes of the official RDNA 2 architecture page and it looks like the previous rumors that claimed the Navi 21 RT performance was on par with the RTX 2080 Ti were not entirely right.
First off, the RDNA 2 architecture page states that the high-performance ray tracing acceleration architecture new to the Navi 21 compute units is called Ray Accelerator. These accelerators are said to provide “an order of magnitude increase in ray intersection performance compared to a software implementation,” a statement that is accompanied by a footnote detailing the process calculating this order of magnitude. The footnote specifies that those measurements were calculated by AMD engineering labs on 8/17/2020 for an AMD RDNA 2 based graphics card. They are not mentioning the exact model, but we can presume it is one of the high-end cards, and looking at the date, AMD surely has managed to further optimize performance in the meantime, at least by a few percent.
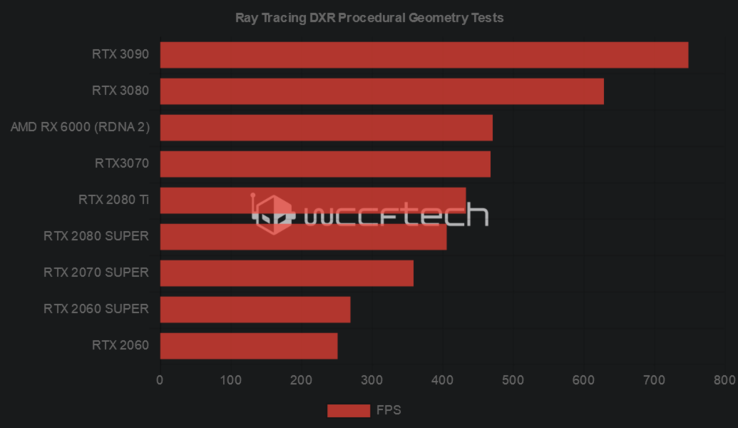
The footnote goes on to say that the measurements were recorded “using the Procedural Geometry sample application from Microsoft’s DXR SDK, [and] the AMD RDNA 2 based graphics card gets up to 13.8x speedup (471 FPS) using HW based ray tracing vs using the Software DXR fallback layer (34 FPS) at the same clocks. Performance may vary.” Now, reddit user ET30 tested his ASUS RTX 3080 TUF card in the DXR SDK and scored 635 fps. Thanks to a graph compiled by the guys at WCCFTech, we can see that the RX 6000 cards are a bit better than the RTX 2080 Ti cards, yet they lag behind the RTX 3080 card by 33%.
Previous 3DMark benchmarks showed that the RX 6800 XT is around 20% slower than the RTX 3080, and we have to keep in mind that both the 3DMark tests and the DXR test are synthetic, so they do not really compare to how RT is actually implemente in games. Thus, AMD is probably not going to deliver Ampere-level RT performance, but at least the RX 6000 cards can be faster than the RTX 2080 Ti cads, which is no mere feat for a first try at ray tracing from AMD.
Source(s)
I nostri Top 10
» Top 10 Portatili Multimedia
» Top 10 Portatili Gaming
» Top 10 Portatili Gaming Leggeri
» Top 10 Portatili da Ufficio e Business economici
» Top 10 Portatili Premium da Ufficio/Business
» Top 10 Portatili sotto i 300 Euro
» Top 10 Portatili sotto i 500 Euro
» Top 10 dei Portatili Workstation
» Top 10 Subnotebooks
» Top 10 Ultrabooks
» Top 10 Convertibili
» Top 10 Tablets
» Top 10 Tablets Windows
» Top 10 Smartphones